how do people use energy? yes in the homes,schools,businesses. the heat the heat in many other homes and businessees comes from electricity.So does the energy to run many common devices,TVs,and waches.
fossil fuels are the ramains of once living things. Coal formed from the remains of dead plants buried in ancient swaps and forests.Natural gas and oil formed from from the remains of tiny ocean plants and animals.
Our supplies of fossil fuels are limited,and fossil fuels are not a renewable energy source.
What other sources of energy are there?
ALTERNATIVE ENERGY RESOURCE:a source of energy other than the burning of a fossil fuel.
MODERN WATERWHEELS(water energy),HARNESSING THE WIND(wind energy),
EARTH FURNACE(geothermal energy).

domingo, 17 de octubre de 2010
martes, 28 de septiembre de 2010
earth rocks soil
rock:a naturally formed solid in the crust, made up of one or more mineral.
igneous rock:a rock formed when melted rock material cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock:a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil:any remains or inprint of living things of the past.
metamorphic rock:a rock formed under heat and pressure from another kind of rock.
humus:decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution:adding any harmful subtances to earth land, water, or air.
rock cycle:rocks changing from one form into another in a never- ending series of processes.
igneous rock:a rock formed when melted rock material cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock:a rock made of bits of matter joined together.
fossil:any remains or inprint of living things of the past.
metamorphic rock:a rock formed under heat and pressure from another kind of rock.
humus:decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution:adding any harmful subtances to earth land, water, or air.
rock cycle:rocks changing from one form into another in a never- ending series of processes.
mineral of earth crust
mineral:a solid material of earth crust with a definite composition.
luster:the way light bounces off a mineral surface.
streak:the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed againt a hard, rough surface.
hardness:how well a mineral resists scratching.
cleavage:the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore:a mineral containing a useful subtance.
gem:a mineral valued for being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource:a resource that can not be replaced within a short period of time or at all
luster:the way light bounces off a mineral surface.
streak:the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed againt a hard, rough surface.
hardness:how well a mineral resists scratching.
cleavage:the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surface.
ore:a mineral containing a useful subtance.
gem:a mineral valued for being rare and beautiful.
nonrenewable resource:a resource that can not be replaced within a short period of time or at all
earth changing crust
fault:a crack in the crust, whose sides show evidence of motion.
geologist:a scientist who studies earth.
magma:hot, molten rock deep below earth surface.
lava:magma that reach earth surface.
weathering:the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces.
erosion:the picking up and carrying away of pieces of rock.
deposition:the dropping off of bits of eroded rock.
meteorite:a chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface(such as earth or the moon).
geologist:a scientist who studies earth.
magma:hot, molten rock deep below earth surface.
lava:magma that reach earth surface.
weathering:the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces.
erosion:the picking up and carrying away of pieces of rock.
deposition:the dropping off of bits of eroded rock.
meteorite:a chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface(such as earth or the moon).
earth and its neighbors
solar system:the sun and the objects that are traveling around it.
planet:any of the eight large bodies that travel around the sun and shine by reflecting its light
gravity:a force of attraction,or pull between any objects and any other objects around it.
hydrophere:earth water
planet:any of the eight large bodies that travel around the sun and shine by reflecting its light
gravity:a force of attraction,or pull between any objects and any other objects around it.
inertia:the tendency of a moving objects to keep moving in a straight line.
lithosphere:the hard,outer layer of earth,about 100 kilometers thick.
crust:the rocky surface that makes up the top of lithosphere.
resource:any material that helps support life on earthhydrophere:earth water
lunes, 27 de septiembre de 2010
solid, liquid and gases
state of matter:any of the forms matter can exist in.
melting point:the temperature at which a solid changes state into a gas.
boiling point:the temperature at which a liquid chauges state into a gas
freezing point:the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid.
melting point:the temperature at which a solid changes state into a gas.
boiling point:the temperature at which a liquid chauges state into a gas
freezing point:the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid.
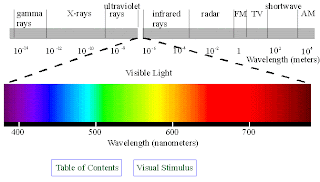
invisible light
electromagnetic:the productionn of magnetism by electricity and the prodution of electricity by magnets.
electromagnetic spectrum:all the wavelenghts of visible and invisible light in order from short(gamma rays) to long (radio).
laser:a device that produce a thin stream of light of just a few close wavelenghts.colors of light
prism:a cutpiece of clear glass(or plastic)with two oppositesides in the shape of a triangle or other geometric shape.
spectrum: a band of colors produced when light goes through a prism.
primary color:red,green,or blue; mixing these colors can produce all the colors of the spectrum.
primary pigment: magenta,cyan,yellow;material with any of these colors absorbs one primary color of light and reflects the other two.
light and lenses
opaque: completely blocking light from passing through.
transparent:letting all light through,sothat objectson the other side can be seen clearly.
translucent:letting only some light through,so that objects on the other side appaer blurry.
polarization:allowing light vibrations to pass through in only one directions.
refration:the bending of light rays as they pass from one subtance into another.
concave lens:a lens that curves outward(is thiker at the edges than at the middle)and spreads light rays apart.
transparent:letting all light through,sothat objectson the other side can be seen clearly.
translucent:letting only some light through,so that objects on the other side appaer blurry.
polarization:allowing light vibrations to pass through in only one directions.
refration:the bending of light rays as they pass from one subtance into another.
convex lens:a lens that curves outward(is thicker at the middle than at the edges)and brings light rays together.
martes, 7 de septiembre de 2010
solar system
inroduction the solar system is the sun and the object traveling around it.
the characterictics of each planets
the distance of each planets to the sun:
Mercury.57.9 Venus.108.2
Earth.149.6 Mars.227.9
Jupiter.778.3 Saturn.1,427
Uranus2,870 Neptune.4,497
Pluto.5,900 .
length of day
Mercury 59 days
Venus 243 days
Earth 24 hours
Mars 24 hours
Jupiter 9 hours 56 minutes
Saturn 10 hours 40 minutes
Uranus 17 hours 14 minutes
Neptune 16 hours 6 minutes
Pluto 6.36 days
conclution
And to conclute I can said that the earth is important for the solar system.
the characterictics of each planets
the distance of each planets to the sun:
Mercury.57.9 Venus.108.2
Earth.149.6 Mars.227.9
Jupiter.778.3 Saturn.1,427
Uranus2,870 Neptune.4,497
Pluto.5,900 .
length of day
Mercury 59 days
Venus 243 days
Earth 24 hours
Mars 24 hours
Jupiter 9 hours 56 minutes
Saturn 10 hours 40 minutes
Uranus 17 hours 14 minutes
Neptune 16 hours 6 minutes
Pluto 6.36 days
conclution
And to conclute I can said that the earth is important for the solar system.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)